When most people think of forklifts they think of the traditional type of forklift that has four wheels, a steering wheel, a gas pedal, and a brake pedal like a car or truck.
The traditional forklift operator sits in a seat much like that of a riding lawn mower and has a set of hand controls to operate the two forks in the front of the machine to lift things.
These traditional forklifts that most people think of have engines that operate on normal gasoline.
There are actually many different types of forklifts that most people are not aware of.
We will go over some of the most popular forklift types here.
Fuel Types
One of the primary things that separate forklifts into different types is the fuel that use.
There are four main types of fuel in use today.
These fuel types are: gasoline, compressed gas, electricity, and diesel.
You will sometimes see gasoline, diesel, and compressed gas forklifts referred to as IC (internal combustion) forklifts.
We will discuss each of these fuel types and the advantages and disadvantages of them.
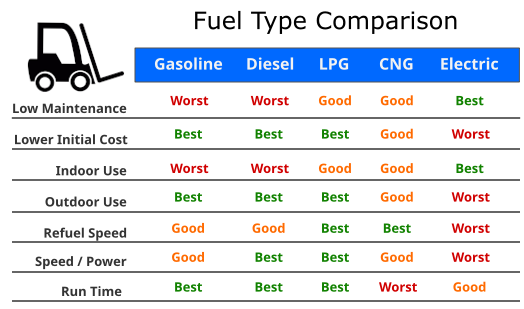
Quick Overview of Fuel Advantages and Disadvantages
We have created a quick chart to show some of the main advantages and disadvantages of different forklift fuel types.
This will give you a quick rundown of the pros and cons of each type of fuel.
If you want more detailed information on what you can expect from forklifts running these different types of fuels then read on for more detailed information.
Gasoline
The first forklift designs primarily used regular gasoline as a fuel source.
This makes sense since regular gasoline is easy to get and relatively inexpensive.
A lot of industrial business locations will have onsite fueling stations or fuel storage tanks that will make it much easier to refuel.
Today gasoline is the least common forklift fuel type you will find.
Gasoline Advantages
Gasoline has several advantages.
As we already mentioned, it is easy to get since there are gas stations all over.
Many industrial complexes have onsite fueling stations if they use quite a few gasoline powered vehicles or equipment.
With gasoline the forklift engine also has a good power output.
Finally, gasoline lasts for a long time between refueling, which saves time.
Gasoline Disadvantages
There are definitely some disadvantages to using gasoline to fuel a forklift.
One of the main disadvantages is that a gasoline powered forklift is not suitable for use indoors unless there is a lot of ventilation available.
This is, of course, due to the exhaust emissions coming from the engine.
There is also more maintenance needed when using gasoline versus some of the other forklift fuel types such as electricity or compressed gas.
This is because gas (and diesel as well), cause more deposits in the engine and also contaminate the oil more than other fuel options.
Diesel
In most places, diesel fuel is pretty easy to get, but it is likely not as prevalent as regular gasoline in many places.
Just as with gasoline, many locations may have onsite fueling available if they use a lot of diesel powered vehicles or equipment.
Diesel Advantages
The advantages to using diesel as the fuel for a forklift are mostly the same as using gasoline to power it as well.
Diesel engines produce more torque than other fuel types, so they are able to perform better on larger inclines or when used on rougher terrain.
Forklifts using diesel as fuel also have the longest run time of any of the fuels covered here.
Diesel Disadvantages
Just as with the advantages of using diesel to fuel a forklift, the disadvantages of diesel are very similar than those for gasoline.
In addition to the gasoline disadvantages diesel has some unique ones of its own.
Diesel engines do tend to be louder when operating than gasoline ones, so that can be a disadvantage.
They also produce soot that can pollute the air and can also build up in the forklift’s exhaust system.
This soot buildup needs to be cleaned out from time to time.
There are some modern forklifts that have methods to catch or eliminate the soot produced by diesel forklift engines, but those usually require extra maintenance.
More maintenance means more downtime where the forklift is not able to be used.
Diesel powered forklifts are only suitable for outdoor use due to their exhaust emissions.
Compressed Gas
Compressed gas has become a very popular way to fuel forklifts.
If you notice you will see many forklifts with a gas cylinder on the back.
That is a giveaway that the forklift is powered by compressed gas.
The two main types of compressed gas used for powering forklifts are compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquid petroleum gas (LPG).
Since both liquid petroleum gas and compressed natural gas are gasses and use a similar type of tank it is easy to get these two forklift fuel types confused.
But there are definite distinct advantages and disadvantages to each of these fuel types.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG)
Compressed natural gas is basically methane that has been filtered and compressed.
You have likely seen blue diamond CNG stickers on some commercial and mass transit vehicles.
This sticker means those vehicles are running on CNG.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Advantages
Compressed natural gas is an environmentally friendly forklift fuel option.
It emits a lower amount of greenhouse gasses as compared to other types of forklift fuels.
It is composed of mostly methane with some nitrogen, carbon dioxide, liquid petroleum gas, and ethane included.
Compressed natural gas also burns cleaner, so it produces less build up in engines.
CNG is lighter than air, so if it leaks is disperses easily and quickly.
It also has an unlimited hold time, so you never have to worry about fuel loss due to old fuel with CNG.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Disadvantages
Probably the main disadvantage of CNG is it needs special equipment to refill tanks, and so that is going to be a large upfront cost if those are not already available.
CNG is less energy dense than gasoline or diesel, so it needs more storage space for the same amount of energy.
Forklifts are fairly small vehicles, so you will not find any huge tanks on them.
This means that you will need to refill CNG tanks more often versus LPG, gasoline, or diesel.
Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Liquid petroleum gas (LPG) is a liquefied gas that is a byproduct created when extracting crude oil.
LPG is heavy, it weighs about twice a much as air.
It is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable explosive gas.
LPG is made up of mostly propane mixed with butane.
Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) Advantages
LPG is is pretty clean burning, and emits less pollution than gasoline or diesel engines.
It has a high octane rating and increases engine life since, like CNG, it produces less engine deposits.
LPG also has a fuel to weight ratio that is the same as gasoline.
It has the lowest initial cost, since all you need to purchase arethe LPG tanks.
Another advantage of LPG is that tanks can be swapped very quickly when refueling.
LPG fueled forklifts are good for both indoor and outdoor environments.
Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) Disadvantages
LPG is heavier that air, so if there is a leak LPG will tend to pool and not disperse unless there is good airflow.
It is also very flammable and explosive, so the fact that it tends to pool and hence concentrate easily means it has a higher chance of causing a dangerous fire or explosion.
Electric
In recent years electricity has been gaining ground in powering of many vehicles.
Everyone these days has heard of Tesla’s vehicles, and many other car and truck manufacturers either have released or plan to release all electric vehicles in the near future.
Forklifts have embraced electric motors for quite some time now, and electric powered forklifts are very common now and have been for some time.
Electric Advantages
Electric forklifts require less maintenance than any other fuel type.
There are no engine oil, engine coolant changes, or engine tune ups needed for forklifts powered by electric motors.
Over time this will be a significant amount of money saved.
Electric powered forklifts have no emissions, so they can be use safely indoors, even in enclosed spaces.
In industries that are sensitive to emissions, such as food processing, this is a very important advantage.
They can also be made smaller and more compact, so they are more maneuverable than forklifts powered by other fuel types.
Electric Disadvantages
There are lots of nice advantages for electric powered forklifts, but there are also disadvantages.
They do cost more upfront for comparable forklifts powered by other fuel types.
Electric forklifts are not well suited for high capacity and high usage applications.
Their batteries also lose power gradually over the course of a shift, so their power output is not consistent over time.
Another disadvantage of electric powered forklifts is the batteries need to be recharged between shifts.
Recharging an electric forklift’s batteries takesseveral hours, and there is usually a cool down period needed before the batteries can use used again.
There are some models and forklift tools that will allow you to change battery packs fairly quickly, so you could purchase multiple battery packs and charge others while one is in use.
But batteries are expensive and take up quite a bit of space, so this is not a very cost effective solution.
Final Thoughts
There is quite a bit to consider when looking at different forklift styles and fuel types.
All of these have different pros and cons that will help dictate the best forklift for your particular application.
There will likely be no perfect solution, but with careful consideration, you will be able to select a good forklift that will serve you will for years to come.







